Sticker Charts!
A great way to motivate your children to behave well and get their homework and chores done!
A visual reminder of chores and appropriate behaviors is critical for children just as many adults need a to-do list.
- Create a chart listing all chores and behaviors that your child should complete by the end of the day.
- Add stickers under each completed chore either at the end of the day or immediately following the chore. Let your child pick out the stickers in order to add to his/her excitement of receiving them.
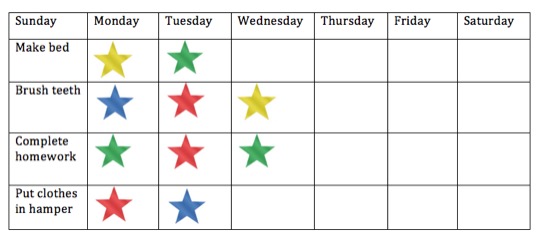
- After a certain number of stickers are earned, reward your child!Many children love to earn the privilege of going to a store and choosing their own toy, for example. Other reward ideas include choosing a movie to watch, choosing a restaurant for dinner, or inviting over a friend each month. Make sure your child knows the rules and rewards for the sticker chart before starting so that he/she is motivated to behave well. Keep the chart somewhere your child can easily see it, such as on his/her bedroom door.Here is an example of a sticker chart for you to use as a model for your own:
Contact Dr. Gordon for help with your ADHD. We have treatment and solutions available online, by phone, and in our offices.
written by: Brianna Malinowski, Jay Gordon, Ph.D