Cavities in Children with ADHD
Children with ADHD have a higher prevalence of dental cavities than children without ADHD. Specifically, children with ADHD are nearly 10 times more likely to have decayed, missing, or filled teeth.
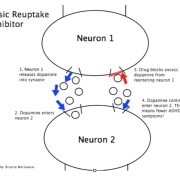
Different theories exist as to why these children experience more cavities and worse oral health in general. Behavior may be to blame for these problems. Factors such as not brushing enough, lack of motivation to maintain oral health, and/or parents using sugary rewards for good behavior may contribute to more cavities. One possibility is that ADHD medication often causes xerostomia, or dry mouth, as a side effect. Since saliva serves as the mouth’s natural protection against cavities, lack of saliva may lead to an increased number of cavities.
A 2012 study examined 3 groups of children; one group had ADHD treated with medication, one group had ADHD not treated with medication, the other group consisted of children without ADHD. If medication causes dry mouth, which leads to cavities, then the ADHD group of children treated with medication would have the highest rate of cavities. However, both groups of children with ADHD had more plaque than the children without ADHD. This suggests that medication is not to blame for poor oral health in children with ADHD.
What can you do to prevent cavities for your child with ADHD?
- Shorter intervals between dental check-ups
- Reduce sugary foods in diet
- Monitor children when they brush their teeth
- Use fluoride rinse after brushing at night
- Do not eat anything after brushing at night
- Use 2-minute hourglass timer to encourage longer brush time
Contact Dr. Gordon for help with your ADHD. We have treatment and solutions available online, by phone, and in our offices.
written by: Brianna Malinowski, Jay Gordon, Ph.D
Rosenberg, S., Kumar, S., & Williams, N. (2014). Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder medication and dental caries in children. The Journal of Dental Hygiene, 88(6), 342-347.