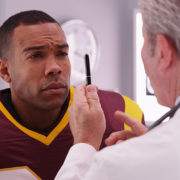
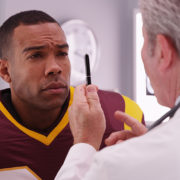
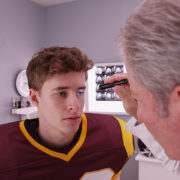
March is Brain Injury Awareness Month. As the month comes to a close, it is important to discuss what causes– and what happens during– a traumatic brain injury (TBI). After all, TBI’s effects over 2.5 million individuals in the United States.
March is Brain Injury Awareness Month. As the month comes to a close, it is important to discuss what causes– and what happens during– a traumatic brain injury (TBI). After all, TBI’s effects over 2.5 million individuals in the United States.
What is a TBI?
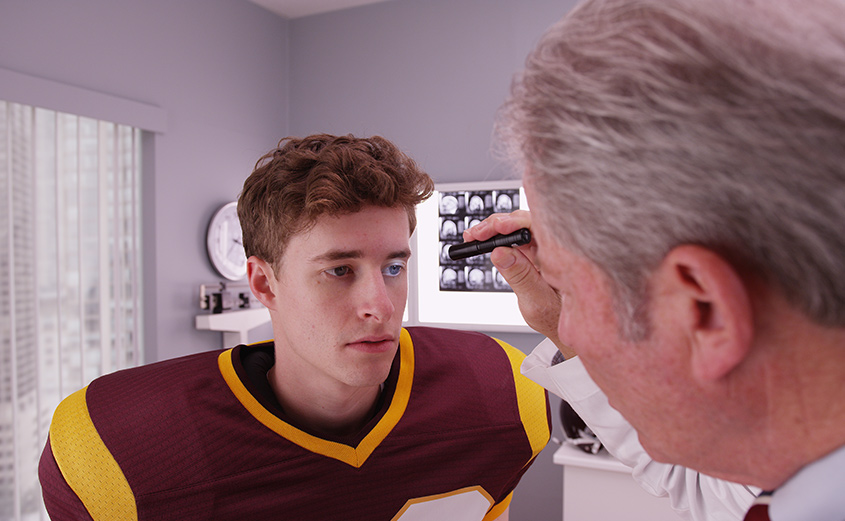
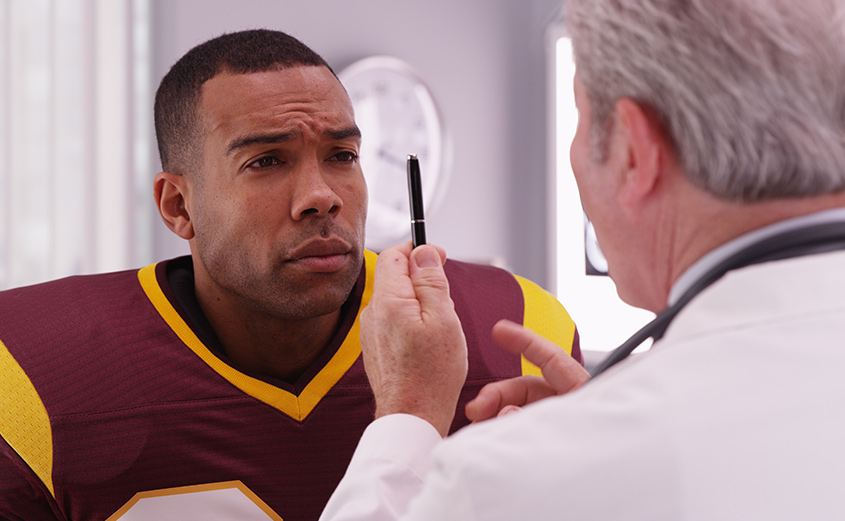
Simply, a TBI is a physical injury to the brain. However, the injury comes from a physical outside impact or the brain’s impact with the skull. A TBI does not refer to hypoxia (lack of oxygen to brain), stroke, or tumor. Instead, the major causes of TBI are falls (28%), car crashes (20%), and blunt force from an object (19%). After initial assault, further damage could be done in what is known as a secondary injury. An example of a secondary injury is restricted blood flow to a region of the brain.
“I am confused. Do I have a concussion or a TBI?”
The short answer is: most likely both! That is because a concussion, by definition, is a type of brain injury often referred to a mild TBI (mTBI). A concussion is therefore a type of brain injury that, depending on the severity, can be quite serious. Sports players are especially vulnerable due to physical contact with the skull. If you are experiencing headaches, fatigue, and/or poor balance, it is wise to make a consultation before continuing intense physical exercise. To learn more about concussions, check out the Pathways website!
What happens to your brain during a TBI?
The human brain is an astonishing organ, weighing in at roughly over three pounds and consisting of 86 billion neurons (brain cells). The texture of the brain can be best compared to that of gelatin. The skull is a hard protective barrier between the delicate brain tissue and the environment. However, when the brain is injured, it swells and fills with fluid just as other parts of the body would. Swelling can cause your brain to push against the skull, causing immense pressure inside the head that could potentially cause further damage, discomfort, and pain.
The neurons of the brain communicate via special messenger molecules called neurotransmitters. These chemicals are in proper balance in order to control mood, sleep, desire, and sense of happiness. A TBI will often disturb this delicate chemistry, resulting in altered emotions and thoughts. Consequently, behavior is often disturbed in those with TBIs.The brain’s chemical balance will often restore itself upon healing. When the injury is very severe, sometimes medications are warranted to intervene in brain’s chemical makeup.
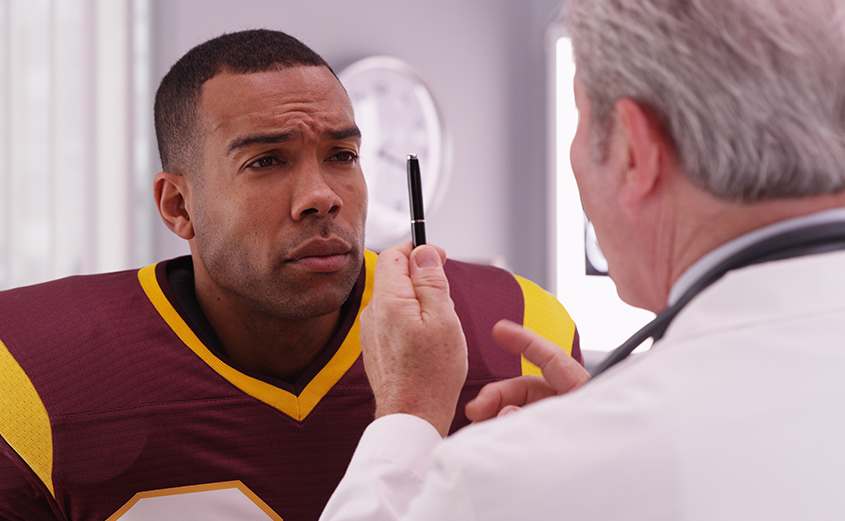
“I am not sure if I have a TBI. What should I do?!”
Professional medical attention is crucial if you are suspicious that you may have a brain injury. Through comprehensive evaluations and sophisticated brain imaging, you can work together with your doctor to heal and prevent further injury.
Check out Dr. Sanjay Gupta of CNN discuss TBIs:






 March is
March is 
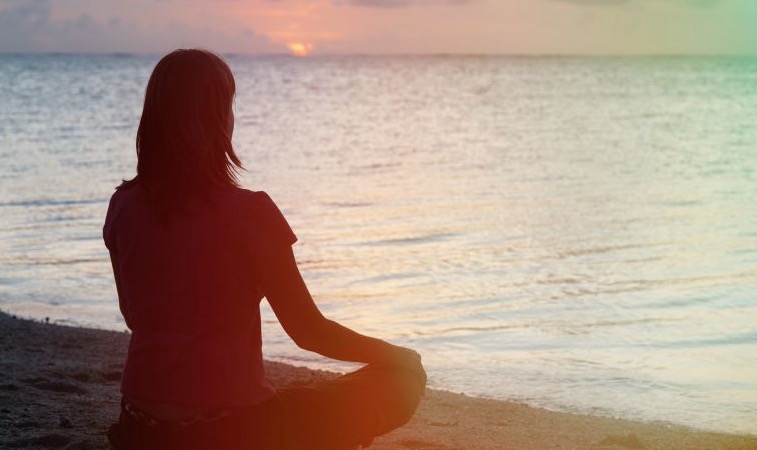



 A new study suggests there’s some science behind the claims made for mindfulness meditation. The benefits of mindfulness meditation, increasingly popular in recent years, are supposed to be many: reduced stress and risk for various diseases, improved well-being, a rewired brain. But the experimental bases to support these claims have been few. Supporters of the practice have relied on very small samples of unrepresentative subjects, like isolated Buddhist monks who spend hours meditating every day, or on studies that generally were not randomized and did not include placebo control groups.
A new study suggests there’s some science behind the claims made for mindfulness meditation. The benefits of mindfulness meditation, increasingly popular in recent years, are supposed to be many: reduced stress and risk for various diseases, improved well-being, a rewired brain. But the experimental bases to support these claims have been few. Supporters of the practice have relied on very small samples of unrepresentative subjects, like isolated Buddhist monks who spend hours meditating every day, or on studies that generally were not randomized and did not include placebo control groups.